Using Python on your own computer¶
To run one of the GLAM Workbench repositories within a dedicated Python environment on your own computer, you need to set up the necessary software. This approach requires familiarity with the command line and the ability to install and manage new software. You will, however, have full control over your working environment.
Setting up your local environment¶
I use pyenv, pyenv-virtualenv, and pip-tools to create and manage Python versions and environments. If you prefer other tools for managing Python environments, adjust the steps below as required.
GLAM Workbench repositories currently use Python 3.10.12, but later versions should be ok. You can install multiple Python versions using pyenv:
pyenv install 3.10.12
Click on the repository's green Code button and copy the web url used for cloning.
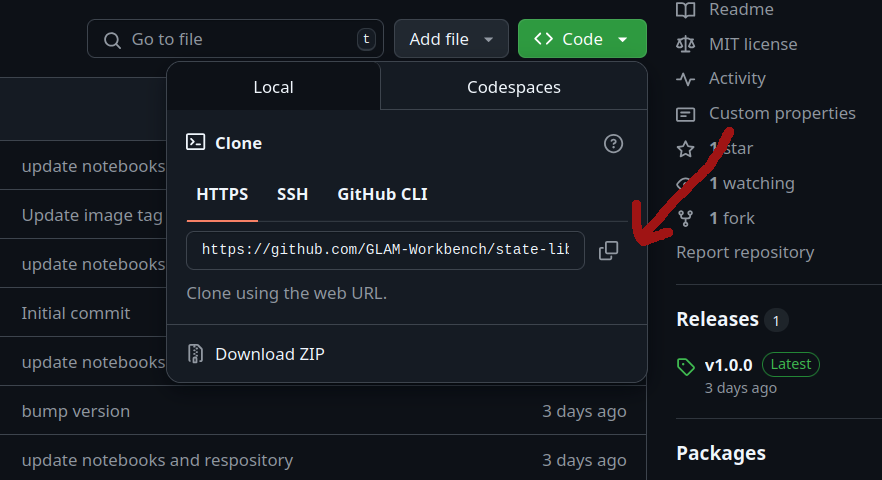
In a terminal, use git clone command to create a local version of the GLAM Workbench repository:
git clone https://github.com/GLAM-Workbench/[REPO NAME].git`
For example:
git clone https://github.com/GLAM-Workbench/state-library-victoria.git`
Use cd to move into the newly-cloned folder:
cd [REPO NAME]
For example:
cd state-library-victoria
Create and activate a Python virtual environment (I find it easiest to name the environment after the repository):
pyenv virtualenv 3.10.12 [YOUR ENVIRONMENT NAME]
pyenv local
For example:
pyenv virtualenv 3.10.12 state-library-victoria
pyenv local
Install pip-tools in the new virtual environment:
pip install pip-tools
Install all the required Python packages using pip-sync:
pip-sync requirements.txt dev-requirements.txt
Running Jupyter Lab¶
- On the command line, run
jupyter lab– to start Jupyter. - A browser window should open automatically. If not, copy and paste the url from the command line to your web browser.
- To shut down your Jupyter Lab session hit Ctrl+C on the command line.
Going further¶
If you'd like to to modify notebooks and contribute the code back to the GLAM Workbench, see Contribute code.
if you'd like to develop your own GLAM Workbench repositories, see Develop a new repository.